Quantum Computing Access @ NERSC
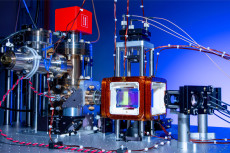
The magneto optical trap at the heart of QuEra's Aquila, a neutral atom system made available to researchers through the QCAN program. (Credit: QuEra Computing)
The Quantum Computing Access @ NERSC (QCAN) program is a first-of-its-kind program to support research on one of the first publicly accessible quantum computers based on neutral atom technology.
Through a partnership between QuEra Computing, competitive proposals are awarded up to 25 hours of quantum computer time, or 270,000 shots, on the company's Aquila neutral atom system.
NERSC and QuEra staff engage deeply with researchers during the project, including biweekly meetings to ensure project goals are met.
Why Neutral Atom Systems?
Neutral atom quantum computers offer distinct advantages in scale and coherence time. Aquila, a 256-qubit analog quantum simulator, can simulate time evolution under the many-body Rydberg Hamiltonian. A white paper on Aquila describes the system’s technical details, including prototypical use cases.
2024-25 Awards
Proposals for the 2024-25 program, running October 2024 through mid-July 2025, were evaluated on the feasibility of the proposed research, alignment with the capabilities and the amount of neutral atom quantum hardware resources available, and benefits to current or future DOE Office of Science research objectives.
Awardees will be announced in October.
Training and Technical Resources
Practical information on using Aquila can be found on QuEra’s online learning platform and a two-day NERSC training held in 2023.
The application programming interface for Aquila is based on Python, either through the AWS bracket or QuEra’s Bloqade API.
Users can take advantage of CUDA-Q, NVIDIA’s high-performance quantum-classical computing platform, with QuEra’s Aquila processor. CUDA-Q’s upcoming integration with Aquila will offer uniquely unified access to CPUs, GPUs, and QPUs (Quantum Processing Units). Allowing programmers to seamlessly integrate QuEra’s Aquila QPU and NERSC’s Perlmutter GPU supercomputer, CUDA-Q supports fully hybrid applications. This focus on accelerated quantum supercomputing empowers developers to explore scalable quantum solutions. Additionally, CUDA-Q’s open-source model and hardware-agnostic workflow means users can trivially switch between QPU hardware and GPU-accelerated simulators, streamlining and expanding application development. The CUDA-Q+Aquila integration will be made available soon.
Contact
Email QCA-NERSC@lbl.gov for further information.
About NERSC and Berkeley Lab
The National Energy Research Scientific Computing Center (NERSC) is a U.S. Department of Energy Office of Science User Facility that serves as the primary high performance computing center for scientific research sponsored by the Office of Science. Located at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, NERSC serves almost 10,000 scientists at national laboratories and universities researching a wide range of problems in climate, fusion energy, materials science, physics, chemistry, computational biology, and other disciplines. Berkeley Lab is a DOE national laboratory located in Berkeley, California. It conducts unclassified scientific research and is managed by the University of California for the U.S. Department of Energy. »Learn more about computing sciences at Berkeley Lab.







