Quantum@NERSC
The possibilities are wide-ranging and inspiring. In the not-too-distant future, quantum information systems are expected to revolutionize how we study disease, design new materials, understand molecular processes, analyze quantum data, and much more.
However, building world-changing quantum information technologies requires interdisciplinary research and development. Fortunately, Berkeley Lab – long known for its team approach to science – is already partnering with industry and academia to fabricate and test quantum-based devices, develop software and algorithms, build a prototype quantum computer and network, and apply these innovations for breakthroughs in a broad range of science areas.
As part of this collaborative effort, the National Energy Research Scientific Computing Center (NERSC) at Berkeley Lab is undertaking multiple endeavors in quantum information focused on topics related to integrating quantum information technologies with HPC technologies.
In 2022, the Quantum@NERSC team established the QIS@Perlmutter program. The inaugural allocation year awarded more than 250,000 Perlmutter GPU node hours to 16 quantum information science (QIS) projects across the U.S. and beyond. Many exciting results illustrate the program’s success. In 2023, the QIS@Perlmutter program awarded over 150,000 GPU node hours to 11 new projects, resulting in many new scientific publications. The program was extended through 2024.
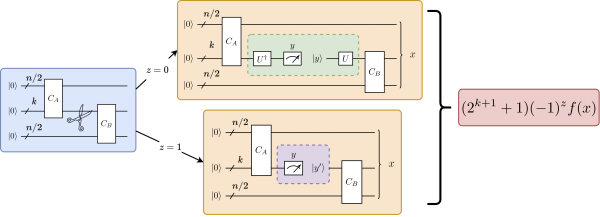
A team of researchers from Xanadu used the QIS@Perlmutter program to develop a new quantum circuit cutting algorithm. The subcircuits CA and CB were simulated accross Perlmutter GPU nodes. (Credit: Lee J. O'Riordan, Xanadu)
Quantum for Science Day, first organized in October 2022, aims to bring together stakeholders from the HPC and Quantum communities and provide a forum to discuss the state of the discipline, including software and hardware advancements.
Further, the Quantum@NERSC team is investigating the potential of quantum hardware through multiple collaborative efforts. An R&D partnership with QuEra Computing is studying using neutral atom quantum simulators for problems in high-energy physics and chemistry.
NERSC sees its role in the budding QIS field as a centralized resource for users who want to bridge the gap between classical computing and quantum computing for applications in chemistry, physics, materials science, drug discovery, and more. Many of the science problems NERSC users are currently focused on are quantum mechanical in nature. By combining classical and quantum resources, NERSC is looking to enhance and expand these research efforts both in the near term and beyond.
For more information about QIS collaborations and resources at NERSC, contact one of the following:
Making Quantum ‘Waves’ in Ultrathin Materials
Running calculations at NERSC, a team of researchers co-led by Berkeley Lab have revealed how wavelike plasmons could power up a new class of sensing and photochemical technologies at the nanoscale. Read More »